Basic Science
Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer
Complication of radiotherapy:
Early
- Skin – erythema, desquamation
- Mucosa – mucositis, dry mucosa
- Candidiasis
- Loss of appetite, nausea, vomitting ( Radiation sickness )
- Laryngeal edema
- Haematopoietic suppression
Late
- Skin – atrophy, fibrosis of subcutaneous tissue
- Xerostomia
- Eye – retinopathy, cataract
- Teeth – decay, osteoradionecrosis
- Trismus ( fibrosis of TMJ and muscles of mastication)
- Endocrine deficit – thyroid, pituitary
- Transverse myelitis
- Radiation induced malignancy – thyroid cancer, osteosarcoma
Why patients undergoing Radiotherapy need to have Hemoglobin level above 10g/dl?
- Low Hb —> low oxygen carrying capacity —> low oxygen —> less radiation-induced cytotoxic free radicals to kill the tumour cells
- Free radicals formation: O2 ——> O+ + O+
H2O ——> O+ + OH-
Is inappropiately high Hb good for radiotherapy?
- No. Increased blood viscosity —-> reduces tumour cell perfusion —–> less free radicals to kill the tumour cells
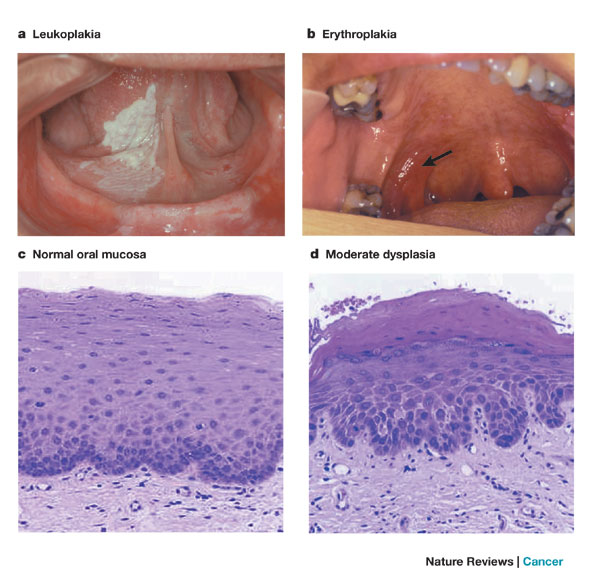
Leukoplakia
Definition of Leukoplakia:
- Premalignant condition
- Characterised by a white patch or plaque that cannot be characterized clinically or histologically as any other disease. (WHO Definition)
How does Verrucous Carcinoma differ from SCC?
Verrucous Carcinoma: “Ackerman’s tumor.” – 1st described by Ackerman
- Uncommon variant of SCC, locally aggressive, clinically exophytic, low-grade, slow-growing, well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with minimal metastatic potential.
- Risk factors: tobacco chewing, oral snuff “Snuff dipper’s cancer”, smoking, alcohol, betel nut chewing
- Good prognosis. Local recurrence is not uncommon, but metastasis to distant parts of the body is rare.
- Painless, thick white plaque resembling a cauliflower (warty lesion)
- Commonest site: Oral cavity
- Treatment: Wide local excision or radiotherapy